Spring 게시판 CRUD 예제
January 21, 2022
오늘은 javaTpoint 에 있는 CRUD예제를 짜보면서 Spring MVC에서 각 요소들이 어떤 역할들을 어떻게 하는지 정리해볼 것이다.
사전작업 - DB table 생성
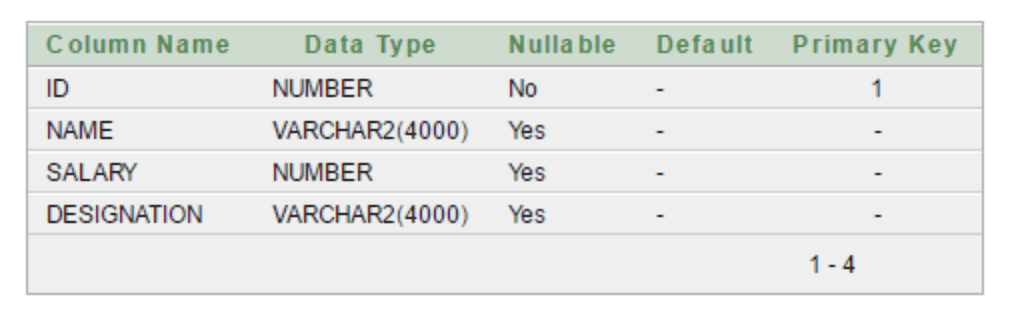
이번에 주어진 예제를 위한 DB table 생성을 위한 mysql 코드는 다음과 같다.
create table Emp99 (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(4000),
salary INT,
designation varchar(4000)
);id는 Null이 되면 안되고, PrimaryKey이며, 그냥 add할 때 편하게 하기위해 AUTO_INCREMENT 옵션을 넣어주었다.
Model
beans
이전에 포스팅했던 자바빈의 형태로 DB에서 받을 데이터의 객체를 만들어 준다. 사전작업에서 올렸던 사진처럼 클래스는 다음의 값들을 가지고 있다.
- id
- name
- salary
- designation
package com.example.crud.beans;
// getter , setter 만 있는 java beans
public class Emp {
private int id;
private String name;
private float salary;
private String designation;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getDesignation() {
return designation;
}
public void setDesignation(String designation) {
this.designation = designation;
}
}getter와 setter만 존재하는 하지만 DB로 부터 받을 데이터 필드는 모두 가지고 있는 클래스 Emp이다.
DAO
이전 포스팅에서 말했지만 DAO는 Data Access Object의 약자이다. 즉 Database에 접근하기 위한 로직을 담는 곳으로 실제 쿼리문들이 여기서 실행된다.
먼저 DB를 사용하고, jdbc를 사용하기위해 아래의 dependency를 pom.xml에 추가해주어야한다.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.11</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency><bean id="ds" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"></property>
<property name="username" value="dbuser이름"></property>
<property name="password" value="dbuser비밀번호"></property>
</bean>- 이후 root-context.xml에 mysql연결정보와 db드라이버를 추가해주어야한다.
package com.example.crud.dao;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import com.example.crud.beans.Emp;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
public class EmpDao {
JdbcTemplate template;
public void setTemplate(JdbcTemplate template) {
this.template = template;
}
public int save(Emp p){
String sql="insert into Emp99(name,salary,designation) values('"+p.getName()+"',"+p.getSalary()+",'"+p.getDesignation()+"')";
return template.update(sql);
}
public int update(Emp p){
String sql="update Emp99 set name='"+p.getName()+"', salary="+p.getSalary()+",designation='"+p.getDesignation()+"' where id="+p.getId()+"";
return template.update(sql);
}
public int delete(int id){
String sql="delete from Emp99 where id="+id+"";
return template.update(sql);
}
public Emp getEmpById(int id){
String sql="select * from Emp99 where id=?";
return template.queryForObject(sql, new Object[]{id},new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Emp>(Emp.class));
}
public List<Emp> getEmployees(){
return template.query("select * from Emp99",new RowMapper<Emp>(){
public Emp mapRow(ResultSet rs, int row) throws SQLException {
Emp e=new Emp();
e.setId(rs.getInt(1));
e.setName(rs.getString(2));
e.setSalary(rs.getFloat(3));
e.setDesignation(rs.getString(4));
return e;
}
});
}
}JDBC 간단 소개
조금 더 많이 편하게 쿼리를 날리기 위해 이 예제에서는 jdbc를 사용하였다. jdbc에 대해 간략하게 소개하겠다.
-
update 문
- 마치 template literal 을 하듯이 중간중간에 값을 넣어주어 쿼리를 만들어주며 이를 template.update(sql)을 통해 실행시켜준다.
- update함수는 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE 쿼리를 실행할 떄 사용하며, 쿼리 실행 결과로 변경된 행의 개수를 리턴한다.
-
queryForObject
- Object jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(SQL구문, 반환 타입, 인자);
-
반환 타입은 데이터 형만 가능하다 (ex, long, int, String) 이렇게 사용된다. 따로 예시를 들면
String name = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject( "SELECT name FROM USER WHERE id=?", String.class, 10);이렇게 id가 10인 레코드의 String타입의 name 필드를 받는 것이다.
-
RowMapper
- 기본형만 받는 것이 불편하여 나왔다. sql문에 따라 추출된 결과를 리턴 받을 객체의 멤버 변수에 적절하게 할당하기위한 매핑 수단이다. 즉 객체로 sql 쿼리문의 결과를 받고 싶을 때 사용한다.
- RowMapper 인터페이스를 implements하여 익명내부클래스로 생성해 사용한다.
Controller
대망의 컨트롤러이다. Controller는 Model과 View를 연결해주는 역할을 한다.
package com.example.crud.controllers;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.example.crud.beans.Emp;
import com.example.crud.dao.EmpDao;
@Controller
public class EmpController{
@Autowired
EmpDao dao; // Autowired태그에 의해 XML 파일에서 DI를 해줄 예정
@RequestMapping("/empform")
public String showform(Model m) {
m.addAttribute("command", new Emp());
return "empform";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/save",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(@ModelAttribute("emp") Emp emp){
dao.save(emp);
return "redirect:/viewemp";//will redirect to viewemp request mapping
}
@RequestMapping("/viewemp")
public String viewemp(Model m) {
List<Emp> list = dao.getEmployees();
m.addAttribute("list", list);
return "viewemp";
}
@RequestMapping(value="editemp/{id}") // @PathVariable은 path에서 받은 변수를 바로 쓸 수 있다.
public String edit(@PathVariable int id, Model m) {
Emp emp = dao.getEmpById(id);
m.addAttribute("command", emp);
return "empeditform";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/editsave", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String editsave(@ModelAttribute("emp") Emp emp) {
dao.update(emp);
return "redirect:/viewemp";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/deleteemp/{id}", method= RequestMethod.GET)
public String delete(@PathVariable int id) {
dao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/viewemp";
}
}- @RequestMapping 은 괄호 안에 값을 request했을 때 실행되는 메소드이다.
- @Autowired는 DI를 해준다. 따라서 EmpDao를 다른곳에서 new를 해주지 않아도 스프링 컨테이너가 알아서 생성주기를 관리한다.
- RequestMapping으로 단순히 Get일 때만이나리ㅏ POST일 때도 구분해줄 수 있고, path에서 받은 변수를 @PathVariable로 사용해줄 수 있다.
<bean id="jt" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="ds"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dao" class="com.example.crud.dao.EmpDao">
<property name="template" ref="jt"></property>위의 두 bean들은 모두 root-context.xml에 추가되어야한다.
- 위의 bean은 우리가 사용한 JdbcTemplate를 추가해준 것이다.
- 아래 bean은 DI를 할 EmpDao에 대한 정보를 스프링에 알려준다.
View
view는 그냥 복사만 해오도록 하겠다. 각 역할들은 jsp를 할줄안다면 쉽게 알 수 있다.
empeditform.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<h1>Edit Employee</h1>
<form:form method="POST" action="../editsave">
<table >
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><form:hidden path="id" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Name : </td>
<td><form:input path="name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Salary :</td>
<td><form:input path="salary" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Designation :</td>
<td><form:input path="designation" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Edit Save" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>empform.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<h1>Add New Employee</h1>
<form:form method="post" action="save">
<table >
<tr>
<td>Name : </td>
<td><form:input path="name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Salary :</td>
<td><form:input path="salary" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Designation :</td>
<td><form:input path="designation" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Save" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>viewemp.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<h1>Employees List</h1>
<table border="2" width="70%" cellpadding="2">
<tr><th>Id</th><th>Name</th><th>Salary</th><th>Designation</th><th>Edit</th><th>Delete</th></tr>
<c:forEach var="emp" items="${list}">
<tr>
<td>${emp.id}</td>
<td>${emp.name}</td>
<td>${emp.salary}</td>
<td>${emp.designation}</td>
<td><a href="editemp/${emp.id}">Edit</a></td>
<td><a href="deleteemp/${emp.id}">Delete</a></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<br/>
<a href="empform">Add New Employee</a>회고
스프링 프레임워크… MVC 패턴 자체도 너무 재밌고 좋은데, 관련해서 환경설정하는 것이 개인적으로 아직 난해하다. 요즘 캠프말고도 또 다른 특강을 듣고 있어서 너무 시간이 없어서 많이 건들지를 못했는데, 역시 좀 많이 건드려봐야할것 같다.