역할 사슬 패턴 (Chain Of Responsibility)
March 10, 2022
역할 사슬 패턴 (Chain Of Responsiblity)
역할 사슬 패턴은 여러 개의 객체 중에서 어떤 것이 요구를 처리할 수 있는지를 사전에 알 수 없을 때 사용한다. 요청 처리가 들어오게 되면 그것을 수신하는 객체가 자신이 처리 할 수 없는 경우에는 다음 객체에게 문제를 넘김으로써 최종적으로 요청을 처리 할 수 있는 객체의 의해 처리가 가능하도록 하는 패턴이다.
역할 사슬을 사용하는 목표는 다음과 같다.
- to avoid coupling the sender of a request to its receiver, by giving more than one object a chance to handle the request. (둘 이상의 객체에 요청을 처리할 기회를 줌으로써 요청의 발신자와 수신자가 결합 되는 것을 방지하기 위해)
- to isolate the clients from knowledge of how responsibilities are assigned. (책임 즉 역할이 할당되는 것에 대한 것을 클라이언트가 알지 못하게 하기 위해)
- A request will be sent to the chain of objects. The request will be handled by a chain of servers until the request is resolved (요청은 각 서버 object들의 체인에 의해서 해결되며, 요청이 해결될 때 까지 각 서버를 방문한다.)
패턴 구조
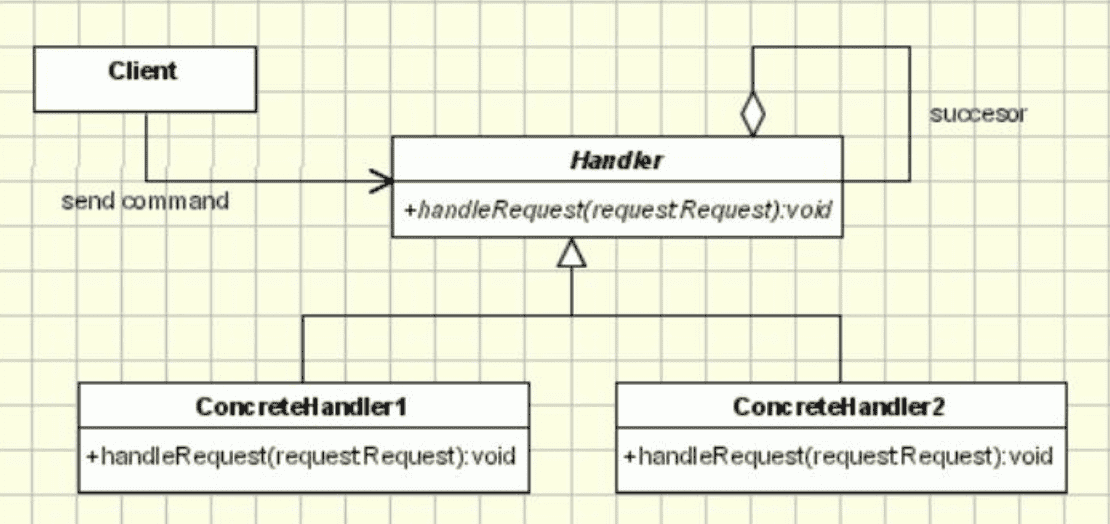
다음 사진처럼 Client는 단순히 request를 부르기만하고, Handler를 통해서 각 Handler에 연결되어 Request를 처리한다.
예제 코드
Main 클래스
프로그램의 메인 실행을 하는 부분이다.
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Support alice = new NoSupport("Alice");
Support bob = new LimitSupport("Bob", 100);
Support charlie = new SpecialSupport("Charlie", 429);
Support diana = new LimitSupport("Diana", 200);
Support elmo = new OddSupport("Elmo");
Support fred = new LimitSupport("Fred", 300);
// setNext를 마치 함수 체이닝하듯이 만들어 역할사슬패턴을 구현.
alice.setNext(bob).setNext(charlie).setNext(diana).setNext(elmo).setNext(fred);
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i += 33) {
// 클라이언트의 request를 표현
alice.support(new Trouble(i));
}
}
}Support 추상클래스
각 사슬이 될 클래스들의 기본 틀이 되는 역할을 한다.
public abstract class Support{
private String name;
private Support next;
public Support(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public Support setNext(Support next){
this.next = next;
return next;
}
// support 함수는 해당 request를 처리하는 함수이다.
public final void support(Trouble trouble){
// 만약 현재의 인스턴스가 resolve 할 수 있다면 done 메서드를 시랳앟ㄴ다.
if(resolve(trouble)){
done(trouble);
// 만약 현재의 인스턴스가 resolve를 할 수 없고, 다음 사슬이 존재한다면, trouble을 다음 사슬에게 넘긴다.
} else if(next != null){
next.support(trouble);
}
// 아무도 처리를 못할 경우 fail을 호출한다.
else {
fail(trouble);
}
}
public String toString(){ return "[" + name + "]"; }
protected abstract boolean resolve(Trouble trouble);
protected void done(Trouble trouble) { System.out.println(trouble + " is resolved by " + this + "."); }
protected void fail(Trouble trouble) {
System.out.println(trouble + " cannot be resolved.");
}
}Support 클래스의 구현클래스들
NoSupport
이름 그대로 resolve를 해줄 수 없는 도움되지 않는 클래스이다. 그렇기 때문에 resolve 메서드가 있을 때 항상 false를 반환한다.
public class NoSupport extends Support {
public NoSupport(String name) {
super(name);
}
// 항상 NoSupport클래스이기 때문에 false리턴한다.
protected boolean resolve(Trouble trouble) {
return false;
}
}LimitSupport
이 클래스는 limit를 넘어서지 않으면 resolve를 해주는 메서드이다.
public class LimitSupport extends Support {
private int limit;
public LimitSupport(String name, int limit) {
super(name);
this.limit = limit;
}
// trouble의 number가 limit보다 작다면 true를 리턴한다.
protected boolean resolve(Trouble trouble) {
if (trouble.getNumber() < limit) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}SpecialSupport
처음 생성될 때 주어지는 특정 숫자만 resolve 할 수 있는 Support 이다.
public class SpecialSupport extends Support {
private int number;
// number 에 대한 숫자를 저장한다.
public SpecialSupport(String name, int number) {
super(name);
this.number = number;
}
protected boolean resolve(Trouble trouble) {
// trouble의 숫자가 해당 Number와 같으면 해결할 수 있다.
if (trouble.getNumber() == number) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}OddSupport
public class OddSupport extends Support {
public OddSupport(String name) {
super(name);
}
// 홀수인 trouble만 해결해준다.
protected boolean resolve(Trouble trouble) {
if (trouble.getNumber() % 2 == 1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}Trouble 클래스
Client 의 request를 담당함
public class Trouble {
private int number;
public Trouble(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public String toString() {
return "[Trouble " + number + "]";
}
}실행결과
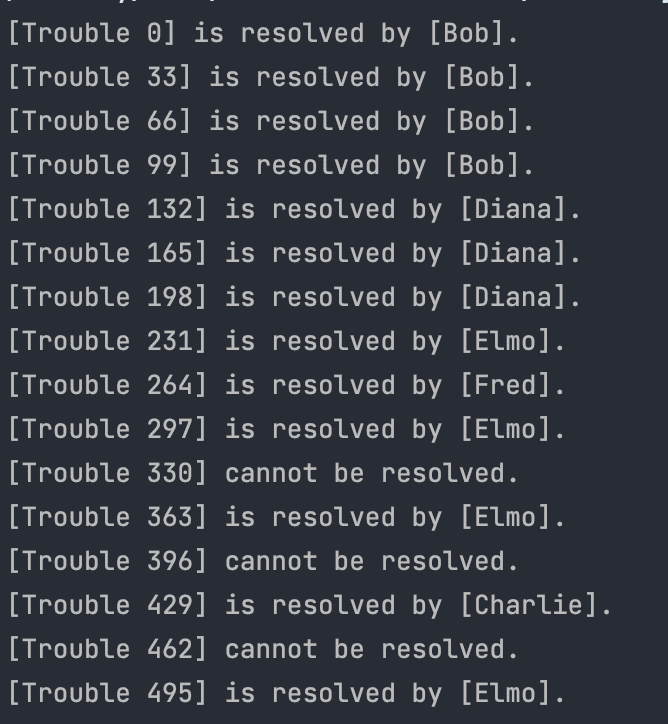
알아야 할것
-
the role of abstract keyword
- abstract keyword를 통해 각 구현 클래스에서 만들어야할 틀을 제시해주었다. abstract 클래스는 그 자체로는 아무런 기능을 하지 못하지만, 이를 구현하여 사용할 때 공통적인 틀을 제공해준다.
- 구현 클래스에서는 abstract 클래스에서 구현한 메서드를 바로 사용할 수 있따.
-
how to chain multiple objects
- abstract class 에서 setNext함수를 통해 마치 링크드리스트를 연결하는것처럼 다음 차례가 될 Support를 연결해주었다.
-
the role of to String() method
- 각 Support 추상클래스의 done이 실행할때 System.out.println 에 this가 들어가 있다. toString메서드는 System.out.println 에서 this가 호출될 때 자동적으로 호출된다.